ETH vs Solana vs Cosmos Staking: A Comparative Guide

Ethereum, Solana, and Cosmos have established themselves as the leading blockchains.
Outside of Bitcoin, the three blockchains support impressive token market capitalization, developer activity, and network performance. These digital assets are prime targets for long-term crypto participants.
Long-term investors holding the tokens of the blockchains can generate passive income through staking.
In this article, we tackle the following:
- Brief history of Ethereum, Solana, and Cosmos
- A comparison of different staking methods
- How to optimize your staking
Ethereum Network
Ethereum switched to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism with the launch of the Beacon Chain last December 2020 and the completion of The Merge in September 2022.
Ethereum’s transition from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) reduced the network’s energy consumption and enabled ETH holders to stake their tokens to secure the network and earn rewards.
Earlier Solo Stakers guides discussed how the Ethereum network relied on high-energy mining hardware. This switch to Proof-of-Stake significantly reduced the Ethereum blockchain’s electricity requirements.
Solana Network
Solana, also called the “Ethereum Killer,” is known for its high speed and low transaction costs. The network is a popular choice for decentralized applications (dApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi) projects.
In its early days, the Solana ecosystem suffered from network congestion and outages, leading to transaction failures. However, the Solana ecosystem has vastly improved and has reliably processed transactions.
Solana uses a Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism. Like Ethereum and other Proof-of-Stake (PoS) networks, Solana relies on validators. However, SOL token holders allocate their Solana tokens to these validators in the delegation process.
Cosmos Network
Cosmos, often called the “Internet of Blockchains,” aims to create an ecosystem of interconnected blockchains that can communicate with one another. Holders can stake ATOM, the native token, to secure the network.
The Cosmos Hub is the first blockchain in the Cosmos Network. It connects other blockchains via the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol, enabling data and token transfers.
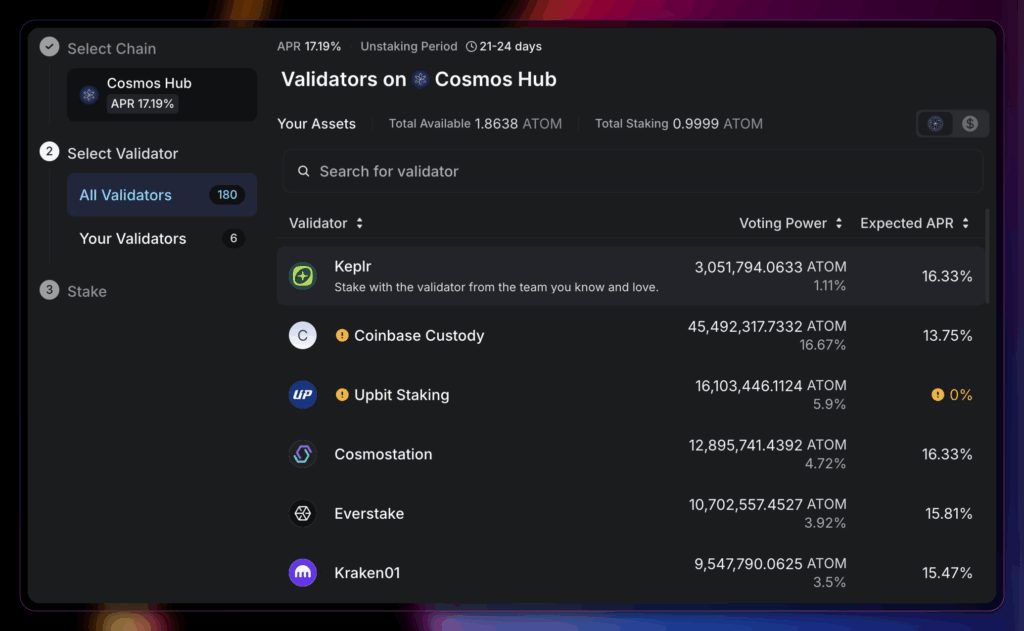
The network uses a Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, where stakers delegate ATOM, the native token, to one of 180 validators who secure the network.
The validator count is capped, so validators compete to secure staked assets. The Cosmos Hub can increase the cap through a governance system.
Staking Methods Comparison
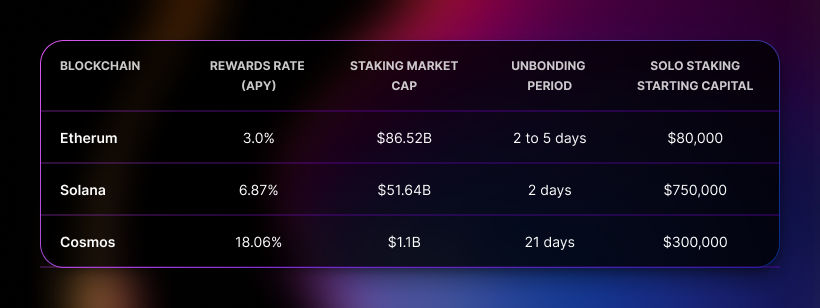
Staking in the three blockchains involves various methods, each offering different levels of participation, rewards, and risks. In addition, the capital required to participate, staking rewards rates, and unbonding periods differ across blockchain networks.
Here’s a comparison of the primary staking methods across these three blockchain ecosystems.
Solo Staking
Solo staking means running your own staking operation or validator node.
Among the three major players, Ethereum is the only ecosystem that reasonably allows solo staking. This type of staking involves setting up a validator to validate transactions and contribute to network security while being profitable.
For solo stakers, Ethereum staking requires a minimum of 32 ETH ($102,400 as of writing) and involves running a validator node. This method gives the staker complete control over their assets and staking rewards. However, it requires technical knowledge and continuous monitoring to avoid penalties such as slashing.
For Solana, the network needs to lower the barriers to entry for people to participate via solo staking.
Solana blockchain staking requires 365 SOL tokens a year (1 SOL token per day) in voting fees. To breakeven, this would imply at least 5,000 SOL tokens ($700,000) at 7% staking rewards per year staked as a solo staker.
To rank among the top 180 validators on the Cosmos blockchain, you would need only $3,000. However, you’re unlikely to break even on maintenance and operational costs at that amount.
Pooled Staking
Pooled staking allows stakers to combine their assets and participate in staking. No minimum stake is required, and users retain custody of their crypto assets.
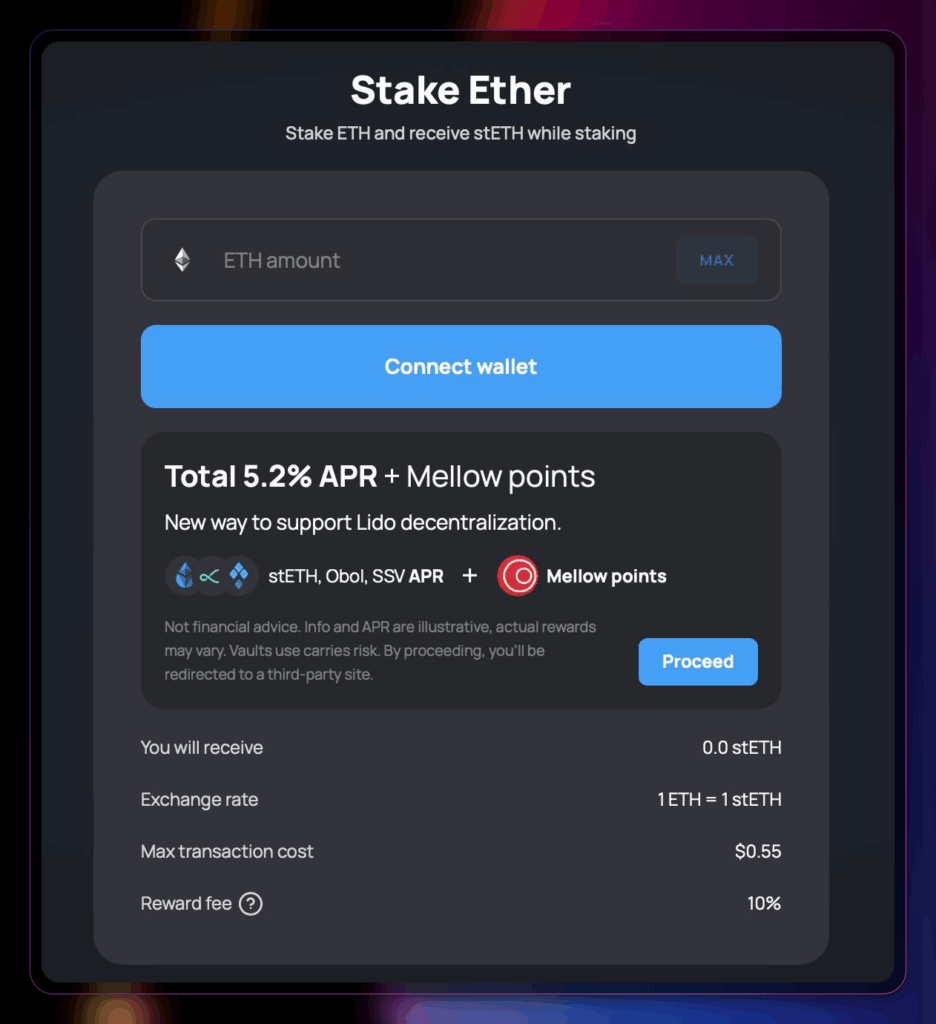
Ethereum staking has evolved to the point where you can perform Pooled Staking directly from your crypto wallet, such as MetaMask, or from a hardware wallet, such as Ledger. This means that as long as you maintain good operational security practices, you can safely participate in the staking process.
For Solana and Cosmos, as they utilize DPoS consensus mechanisms, stakers naturally pool and delegate their assets to validators. You can use crypto wallets such as Phantom and Keplr to stake.
Centralized Exchange Staking
Many centralized exchanges such as Coinbase and Kraken offer staking across several networks, not just Solana and Ethereum. Users can stake tokens directly on the exchange without worrying about technical details.
The downside is lower rewards due to the exchange’s commission rate. Centralized exchanges often have the highest commission rates in the staking industry. The custodial risk of trusting a centralized entity with your assets also exists.
Liquid Staking
Liquid staking rose to prominence for the Ethereum network with platforms like Lido Finance. In Lido, you receive a liquid staking token (stETH) representing your staked ETH. You can utilize these liquid staking tokens (LSTs) in various DeFi protocols to maximize staking rewards and yield. However, this method has inherent risks, particularly those associated with smart contracts.
On the Solana network, Jito Network users receive JitoSOL, an LST that can be used across multiple DeFi projects.
Cosmos differentiates itself by offering liquid staking through platforms like Stride. Users may stake from multiple Cosmos ecosystem networks, such as Celestia and Injective, and receive the Stride token in return.
Cosmos liquid staking distinguishes itself from Solana and Ethereum by supporting many-to-one tokens. You can stake a variety of Cosmos-based tokens for liquid staking. Other platforms only support one staking asset, whether Solana or Ethereum.
Restaking
Restaking is an emerging concept popularized by platforms like Eigenlayer. The platform allows Ethereum stakers to reuse their staked ETH to secure additional protocols or applications. Solana is also exploring restaking through platforms like Solayer.
While Solana and Ethereum share the current spotlight in restaking, Cosmos has been pioneering this concept since early 2023.
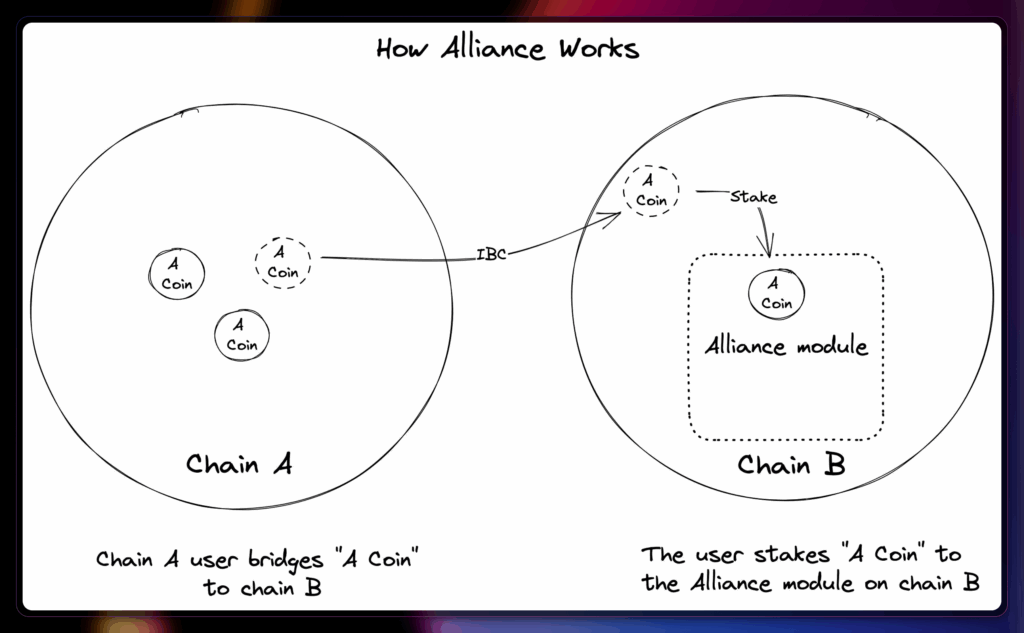
Alliance is an open-source Cosmos SDK module that leverages interchain staking.
According to the documents:
“In simple terms, the Alliance module enables multiple assets to be staked on a chain.”
Currently, stakers can use a handful of native and decentralized finance tokens to secure the Luna Network. The grand vision is that, eventually, users can use all Cosmos-based tokens, including liquid staking tokens, to secure the Cosmos chain.
Restaking is still in its early stages but shows promise. Ecosystem participants laud its ability to leverage existing chain security and offer additional staking rewards.
Staking Optimization
All three networks support staking optimization, including liquid staking and restaking. These methods can significantly boost the yield on your crypto assets.
However, only Cosmos features native staking platforms that offer optimization.
Polli.co is a non-custodial staking optimization platform that offers above-market returns. The platform uses its artificial intelligence (AI) agents to redelegate your tokens and auto-compound rewards automatically.
As a simpler form of staking optimization, you can also choose commission-free or low commission staking pools and validators.
Final Thoughts
Staking is a powerful way to generate passive income through staking rewards.
From an investment perspective, choosing large blockchains such as Ethereum, Solana, and Cosmos increases your probability of success. They are well adopted by developers and will likely survive the various crypto cycles.
By learning the ins and outs of staking within each blockchain, you can select the right blockchain and staking method that suits your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Blockchain Offers the Best Staking Rewards—Ethereum, Solana, or Cosmos?
Solana and Cosmos offer higher base rewards than Ethereum, but Ethereum provides more mature liquid staking options. Cosmos often delivers the highest yields when combined with liquid staking or optimization tools.
Is Solo Staking Worth it on any of these Networks?
Solo staking is only realistic on Ethereum unless you’re operating with substantial capital. Solana requires a high voting-fee overhead, and Cosmos’s low validator cap and operational costs make it difficult to turn a profit.
What’s the Safest Way to Stake Across These Blockchains?
Solo staking is the safest way, as you remain in control of the entire process. Pooled staking through reputable wallets, specifically a hardware wallet, is also a safe option because you retain custody of your assets. Liquid staking offers flexibility but adds smart contract risk. Centralized exchange staking is easiest but also the riskiest due to custodial exposure and lower returns.
Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in February 2024 but has been updated with new information
The content of solostakers.com is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. It represents the personal views and opinions of the author(s) and is not endorsed by any financial institution or regulatory body. Cryptocurrency and staking investments carry inherent risks and readers should conduct their own research and consult with a financial professional before making any investment decisions. The owner and author(s) of solostakers.com will not be liable for any losses, damages, or consequences arising from the use of the information on this site. By accessing solostakers.com, you agree to bear full responsibility for your investment decisions.
September 6, 2024
November 21, 2025