What is Staking: The Basics and Benefits of Crypto Staking

Who doesn’t dream of making money from their crypto portfolio while sleeping?
Staking crypto makes this dream a reality.
Staking has become so popular that the global staking market capitalization stands at $206 Billion as of this writing. This value is just outside the top 25 largest banks in the United States by assets.
But what is staking? And why have so many people jumped on board this concept?
In this article, we break down the following:
- What is staking?
- Benefits of staking
- Different staking types
- Risks and challenges
If that interests you, get ready to dive in.
What is staking?
Proof of Stake (PoS) Staking
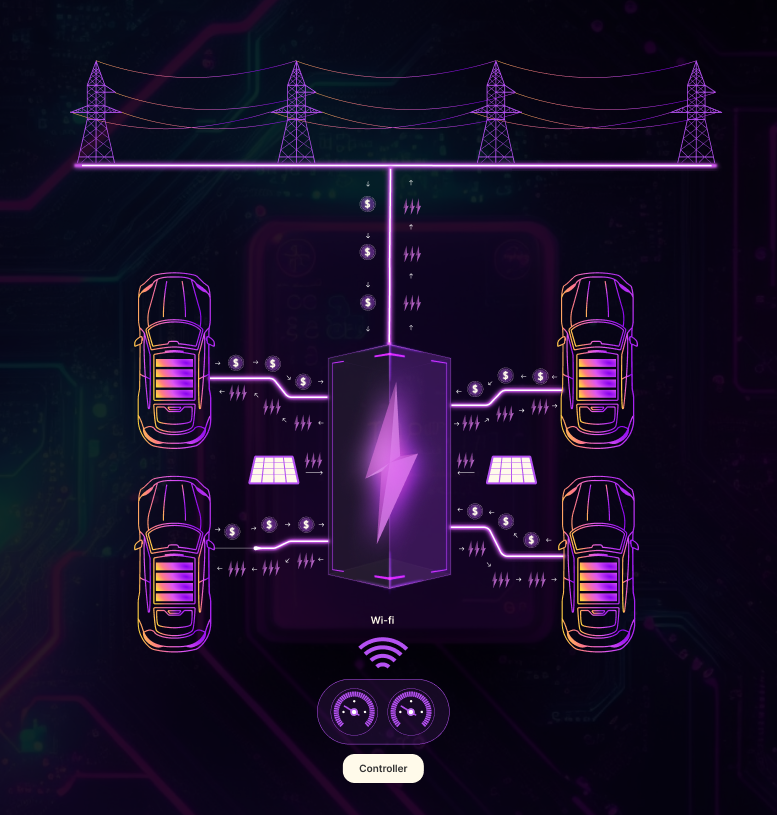
Consider staking, such as installing an electric vehicle (EV) charging station. Through this station, you contribute directly to the EV infrastructure and help make the world free from fossil fuels. Other EVs can charge at your station, and you receive payments.
Crypto stakers operate similarly.
In staking, you set up a computer that connects to the blockchain and contributes to the overall network infrastructure. Then, you deposit a portion of your cryptocurrency to support the operations of the said network. In return, you receive staking rewards determined by the amount and duration of the coins you stake.
For example, crypto staking on Ethereum, the 2nd-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, can earn 2.8% per year. If you placed 32 ETH, you’d get back around 0.0896 ETH rewards after a year.
Multi-Asset Staking (MAS)
Picture multi-asset staking as placing your money in a peer-to-peer lending platform. Such platforms allow individuals to lend their money to others in exchange for interest payments. Borrowers hopefully make good use of your money in their creations or business operations, and you will receive the rewards.
In MAS, a user may deposit cryptocurrency X but receive reward Y, which gives rise to the term multi-asset.
Lava Network, a decentralized RPC protocol, allows users to stake and restake their LAVA tokens and receive a diversified basket of crypto.
In this guide, we will discuss Proof of Stake (PoS) Staking.
Why Go Proof of Stake?
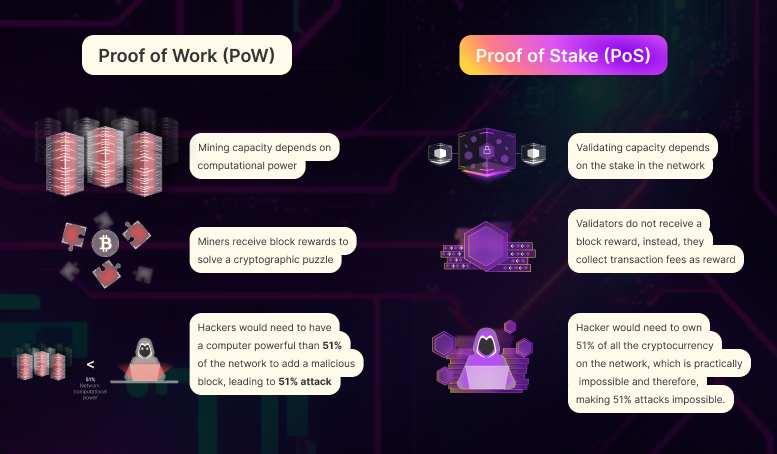
Traditionally, blockchains used proof-of-work (PoW) mechanisms to verify transactions on the network. Also called mining, PoW requires significant physical hardware and substantial electricity consumption.
The high energy costs have led miners to flock to countries with more affordable electricity. At the same time, hardware has been getting expensive. Mining operations eventually focused on a few players, turning what is supposed to be a decentralized activity into a centralized one.
Newer blockchain networks adopted the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, otherwise known as staking, to address these high energy costs.
While physical infrastructure is still needed to run the system, staking crypto does the heavy lifting. You then become an active participant in the network, helping to validate transactions and secure the blockchain.
Under staking, physical hardware is not that important. Instead, the amount and duration of coins you staked play a significant role.
Benefits of Staking
Aside from keeping the network secure and operational, crypto staking provides many other positives.
Earn Passive Income
Staking allows you to earn passive income by locking up your cryptocurrency in a blockchain. In return, you receive staking rewards in the form of additional tokens. This passive income opportunity is an excellent way to generate consistent returns on your investment, especially if you aren’t into trading.
Participate in Network Governance
Many blockchain networks that support crypto staking also allow participants to participate in network governance. Stakers vote on proposals or changes to the network’s protocol, giving you a voice in shaping the blockchain’s direction.
SUI Network allows token holders to submit and vote on proposals.
Reduce Energy Consumption
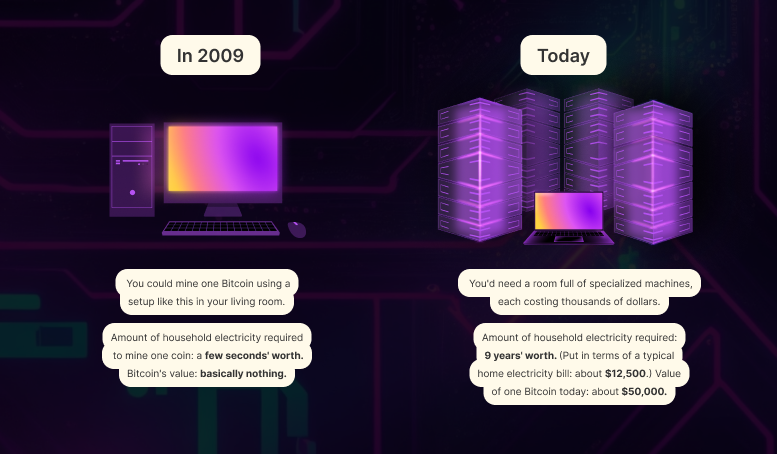
When Bitcoin first came onto the scene in 2009, a person could mine several bitcoins from their desktop. Nowadays, companies set up warehouses of machines to mine a single bitcoin.
With crypto staking, a person needs to set up a single computer, hold crypto in their wallet, and lock it up in the blockchain network. Stakers can stake from home.
Furthermore, staking encourages long-term holding of cryptocurrencies, reducing market volatility and creating a more reliable market.
Different Types of Staking
When it comes to staking your crypto assets, a handful of options exist for you to earn rewards. You must evaluate each option’s reward structure, technical difficulty, and security.
Solo Staking (AKA Self Staking)
Under this method, a crypto holder stakes their tokens on a blockchain without relying on a third party or a staking pool.
Let’s use Ethereum, a PoS blockchain network, as an example:
- Users must set up their node, which operates and stores a copy of the Ethereum blockchain. A node can run on a single computer and operates 24/7. Nodes contribute to the network’s overall decentralization by having various machines worldwide store copies of the network’s data. While you may not be earning staking rewards as a node operator, you still play a significant role in the overall health of the blockchain.
- You must turn this node into a validator to earn a staking reward. You must deposit 32 ETH (over $100,000 in today’s prices). Validators verify the transactions on the network. By having a deposit, you now have skin in the game. Malicious validators can lose their entire deposit.
- In return for validating transactions, the staker receives transaction fees as fresh ETH.
Solo Staking is the most secure method, as it cuts out middlemen and lets you retain direct crypto ownership. However, it’s also the most complex. This high capital entry and comfort level with computers may bar people from pursuing self-staking.
Staking Pools
Under pooled staking, a staker combines their staked tokens with those of other stakers to help validate networks.
Coinbase and Robinhood, centralized exchanges, operate crypto staking platforms. Customers stake their tokens together with other customers.
Exchanges combine the deposited tokens perform network validation.
With their technical ease and lower capital requirements, staking pools have become popular options among crypto stakers. In the Cosmos network, Coinbase is the largest validator, holding staked customer tokens.
Staking vs. Mining
Staking (Proof-of-Stake) and Mining (Proof-of-Work) are different methods for validating transactions and securing blockchain networks. Earlier cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, relied on mining. Newer crypto, such as Ethereum, Solana, and Cosmos, use staking.
Mining
Miners race against each other to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions (stored in a block) and receive new coins as a reward.
The original creator programmed Bitcoin rewards to halve roughly every 4 years (known as Bitcoin halving). As a result, miners become even more competitive and upgrade their computer equipment or pool together. This arms race for the most computing power requires large energy consumption.
Staking
A PoS consensus mechanism similarly involves nodes in validating transactions and securing the network. Instead of how much computer power you have, the rewards are handed out based on the number of coins and the duration you stake.
Staking is considered to be more accessible than mining, as it requires less specialized hardware and technical expertise.
Risks and Challenges of Staking
While staking offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to be aware of the risks and challenges involved:
Market volatility
Staking yields are dynamic and reflect the network’s staking stats. A drastic change in network metrics and token prices can impact the value of your assets and diminish your crypto income.
Technological risks
Proof-of-stake consensus relies on smart contracts, which are self-executing. A protocol may have smart contract flaws, such as delays or freezes in sending staking rewards.
PoS validator nodes could also vote poorly or try to attack the network by halting and possibly reversing transactions. Those are rare, however, and PoS has made it difficult for attackers as it would require owning 51% of the network’s token supply.
Regulatory uncertainty
Global regulators have yet to familiarize themselves with cryptocurrency. As such, many governments have yet to solidify their policies around it.
U.S. regulators have taken a very positive stance on cryptocurrencies and staking since 2024. However, this was not always the case.
In February 2023, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) alleged that crypto exchange Kraken sold unregistered securities through its staking-as-a-service offering. The SEC ordered the shutdown of Kraken’s US-based staking operations and a $30M fine.
Many more significant risks exist. That’s why thorough due diligence is essential before committing to stake crypto.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Storage of Cryptocurrency
You may have heard of the famous phrase, “Not your keys, not your crypto.”
Opening a crypto exchange account and depositing your digital assets into the platform can be tempting. These big exchanges take hold of your crypto, safeguard it, and offer you a wide range of services.
However, should anything happen to the platform or worse, should the people operating the exchange act maliciously, you’ll most likely lose all your assets as the exchange ultimately handles it. Such was the case of FTX, the previous 2nd-largest crypto exchange.
On the other hand, decentralized crypto wallets enable you to retain ownership of your cryptocurrency. As long as you safeguard your keyphrase, even if the company behind the crypto wallet goes down, you can still access your cryptocurrency through another wallet, as your keyphrase gives you direct access to the blockchain.
You can classify decentralized wallets into hot, cold wallets, and hardware wallets.
Hot Wallets
Hot wallets are convenient and can connect to the internet and decentralized applications. You can download these applications from any computer worldwide with your keyphrase. Famous wallets such as Metamask and Phantom Wallet come to mind.
Hardware Wallets
Meanwhile, hardware wallets are devices designed to securely store cryptocurrency. They usually come as a USB and only access the internet once you connect it to a computer. Brands such as Ledger and Trezor have made a name for themselves through these devices.
Cold Wallets
Finally, cold wallets are paper- or file-based wallets that store one’s keyphrase and crypto address. Yes, you read that right – you can create your cold wallet by handwriting or printing your keyphrase on a piece of paper and locking it up in a vault. Similarly, it could be a text file stored on a USB.
That’s not to say these methods are foolproof. Malicious actors constantly prowl to drain an unsuspecting user’s wallet. Mark Cuban lost nearly $1 million in crypto after downloading an unsafe version of MetaMask.
Is Crypto Staking Worth It?
Crypto staking is worth it if you’re willing to do thorough research, understand the risks involved, and choose the right cryptocurrency and staking methods. Staking can be rewarding and profitable. It allows you to actively participate in the blockchain ecosystem while potentially earning additional tokens and generating a passive income stream.
However, the crypto space comes with many risks. Crypto staking is not a guaranteed way to earn income and may result in capital losses.
Many new blockchain networks have launched, encouraging holders to stake their tokens. Unfortunately, these token prices have fallen from 50% to 80% of their original value, more than outweighing the staking rewards.
On the other hand, more established networks, such as Ethereum, have kept staking rates low while maintaining their token prices. Stakers would profit from such networks.
So, if you’re ready to unlock the potential of staking and take advantage of its benefits, start exploring the staking world today.
Happy staking!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Staking and How Does It Work?
Staking is the process of locking your cryptocurrency to help secure and operate a blockchain network that uses a Proof-of-Stake consensus. By staking your tokens, you help validate transactions and maintain the network. In return, you earn staking rewards, usually paid in the same cryptocurrency.
Is Staking Crypto Worth It?
Staking can be worth it if you adopt a long-term mindset and choose the right network. However, staking rewards can be outweighed if the token’s price drops significantly. Established networks with stable ecosystems tend to offer lower yields but lower risk.
Is Staking the Same as Gambling?
No, staking is not the same as gambling. Gambling relies on chance, while staking is a structured process tied to blockchain participation. Staking rewards are determined by clear rules, including stake amount, duration, and network conditions.
Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in October 2023 but has been updated with new information.
The content of solostakers.com is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. It represents the personal views and opinions of the author(s) and is not endorsed by any financial institution or regulatory body. Cryptocurrency and staking investments carry inherent risks and readers should conduct their own research and consult with a financial professional before making any investment decisions. The owner and author(s) of solostakers.com will not be liable for any losses, damages, or consequences arising from the use of the information on this site. By accessing solostakers.com, you agree to bear full responsibility for your investment decisions.
January 19, 2026
January 24, 2026