Understanding the Staking Market: Overview for Crypto Investors

Crypto staking has emerged as an opportunity for investors to maximize returns on their digital assets.
You can stake crypto on platforms to help secure the network and operations of a chosen blockchain. In return, you earn passive income. However, as blockchain rapidly advances, you can find yourself lost in the new tech and jargon.
That’s where we come in to help.
In this article, you’ll learn the following:
- What is staking
- The crypto staking market size
- Different segments of the staking market
- Staking benefits and risks
…and more.
Let’s get started!
What is Staking and How Does It Work?
Staking is a consensus mechanism to verify transactions on a blockchain network.
Stakers set up computer hardware (called a node) that connects to the blockchain, adding to the overall network infrastructure. They then stake a portion of cryptocurrency to validate network transactions. Finally, stakers receive rewards determined by the amount and duration of the tokens staked.
Interestingly, blockchain developers first proposed staking in 2012 as an alternative to mining used for Bitcoin’s consensus mechanism. Mining, to this day, requires expensive hardware and high electrical consumption.
Peercoin, the first cryptocurrency to support staking, appeared in 2013. Blackcoin, the first pure staking protocol, followed in 2014. While neither project remains relevant today, they paved the way for the current staking-based networks such as Ethereum and Solana.
How Big is the Staking Market?
The staking industry has grown to over $250 billion as of January 2026.
Ethereum staking (ETH) holds the majority market share, with $119 billion in staked assets. Solana and BNB follow suit with $62 billion and $24 billion, respectively.
In terms of staking types, traditional staking (whether solo staking or through delegations, or staking-as-a-software provider) continues to dominate the market. In addition, liquid staking and restaking have emerged as alternatives.
As of writing, investors have invested over $85 billion in liquid staking and restaking platforms.
Different Segments of The Staking Market
Solo Staking
In Solo Staking, participants stake their tokens on a blockchain network without relying on a third party.
In a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network, a staker sets up their own computer that runs a copy of the blockchain software. By staking the required cryptocurrency, the node becomes a validator, verifying transactions on the network. A staker then receives native tokens as rewards.
Critics have commented that PoS networks are too expensive for the normal crypto participant.
In Ethereum staking, the most popular option for solo staking, stakers must deposit 32 ETH (over $100,000 at today’s prices). As such, third-party staking mechanisms have risen to address this affordability issue.
Delegated Staking
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) works similarly to Proof of Stake consensus but eases the financial requirements of POS staking.
Stakers pool their tokens together and assign these to a delegate. The delegate with the most staked tokens will go on as the chosen validator (also known as a witness) and earn staking rewards.
In this manner, a staker does not need thousands to participate in securing a blockchain network. Solana and Cosmos serve as great examples of DPoS networks.
Despite its benefits, critics have noted that this delegation system tends to centralize cryptocurrency in the hands of a few large players.
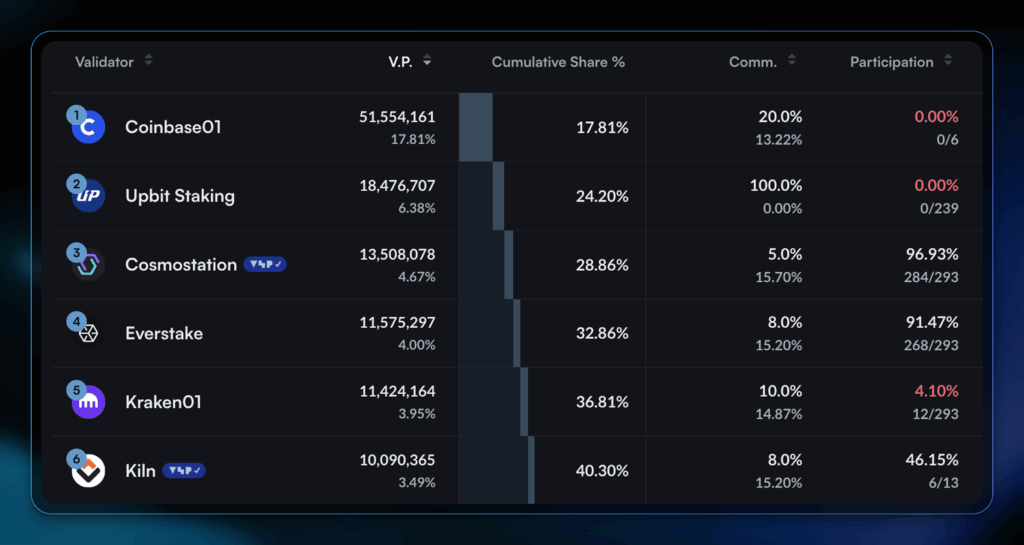
In the case of Cosmos, the top six validators control 40% of total staked ATOM.
Staking as a Service Platforms (SaaS)
SaaS platforms handle the hardware and software requirements while users provide the staked tokens.
A staker maintains complete control over their staked assets by holding the withdrawal keys. They hand over the validator keys to the third party for validation. If the third party does not maintain the node properly or mishandles validation, the staked assets could be penalized.
Stakefish and Allnodes have grown in popularity, especially for ETH staking. Their ease of use and staking dashboards have attracted numerous users. Both platforms support hundreds of thousands of staked ETH.
Liquid Staking
Liquid staking falls under third-party staking.
Users stake their cryptocurrency on a third-party platform or centralized exchange, which pools the staked tokens for network validation. Users then receive liquid staking tokens (LST), equivalent to their staking capital.
LSTs represent a user’s staked tokens on a blockchain network. Users can deploy these liquid staking tokens to other protocols for trading or to generate more yield.
This immediate liquidity has made liquid staking protocols a favorite amongst crypto investors.
Lido Finance dominates the liquid staking market with $29 billion in total value locked.
Ethereum and Solana have attracted the most capital and innovation in liquid staking.
Restaking
Restaking is a process in which you can use already-staked assets, such as ETH and SOL, to secure other decentralized applications. Restaking, across other networks, is also known as redelegation.
Think of restaking as a way to earn extra staking returns.
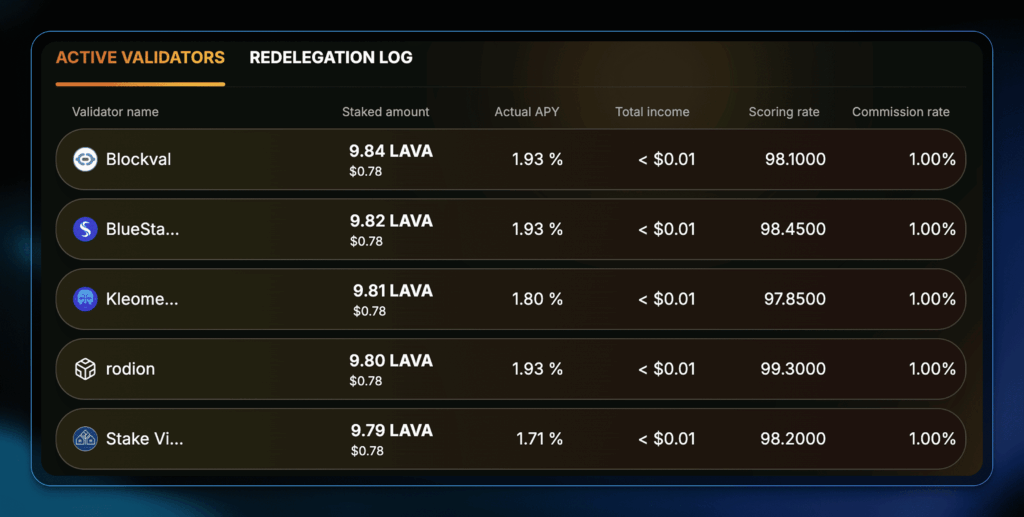
In the case of Lava Network, a decentralized data network, native staking gives you less than 2% APY.
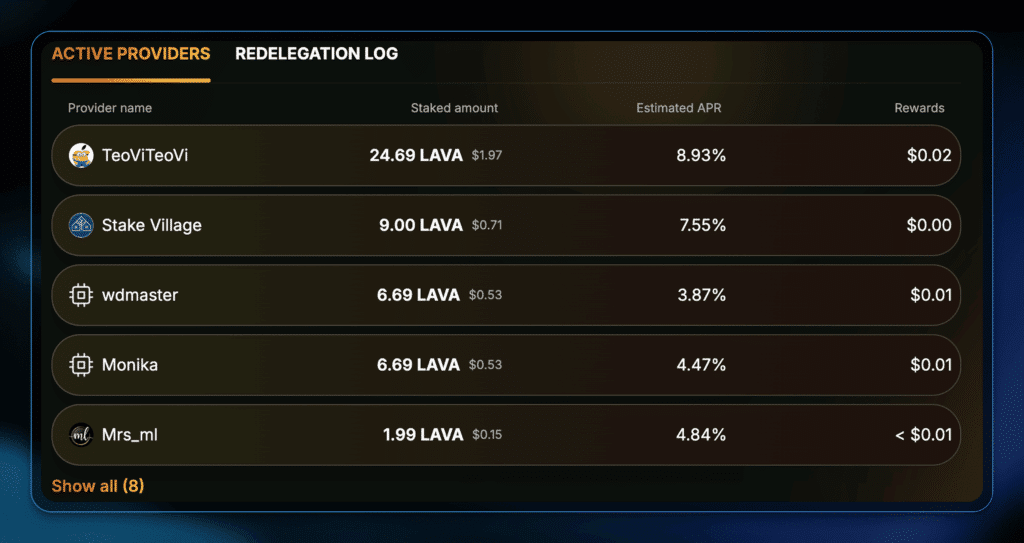
However, through redelegation, you get an extra 4% to 9% on your LAVA tokens. You can then grow this yield even further with a staking optimization platform like Polli.co.
The extra returns differ across blockchains, so make sure to check out the restaking returns for any opportunities.
Staking ETFs
Staking ETFs are regulated financial products that pool investors’ money to purchase and stake digital assets. Investors can buy and sell ETFs through official stock exchanges.
The first staking ETFs launched in 2025, allowing institutional investors to participate in the crypto industry. Investors can easily buy the ETF through an exchange and benefit from staking returns.
The ETF’s issuer handles the technicalities of staking, from buying and securing the digital assets to staking them on the network.
Potential Benefits for Crypto Investors
Staking primarily served as an alternative to mining and has evolved into a new financial industry. Staking now falls within the broader decentralized finance (DeFi) industry.
DeFi has similarly grown beyond Ethereum and caters to other networks and product types.
Passive Income
Before staking, crypto investors held their digital assets and profited only from their sales. Now, a staker also earns yield on their investments.
Ethereum staking and Solana staking offer 3% to 6% APY (annual percentage yield). Other smaller blockchain networks, such as Cosmos, provide APYs of over 17% to entice stakers to their platforms.
Outsized Returns
New staking protocols often reward early users with native tokens as a reward. Stakers earn both staking rewards and native tokens, potentially maximizing their portfolio returns.
JITO Network, the largest liquid staking platform on Solana, offered its native token, JTO, to users who staked SOL on its platform. JITO released over $225 million worth of tokens to early users.
After airdropping the token to users, JTO immediately listed on multiple crypto exchanges. Stakers earned a single-digit yield on SOL and tens of thousands of dollars in additional JTO rewards.
Risks Associated
Staking can seem like a great way to safely earn passive income. However, there are no risk-free returns. Be on guard against staking risks.
Malicious Attacks
Staking platforms operate via smart contracts (self-executing code).
Bad actors have targeted DeFi applications and platforms. Malicious links look to prey on unsuspecting investors. At the same time, attackers swoop in to exploit the technology or drain tokens from the platform, leading to capital losses for users.
In November 2024, a hacker exploited DeFi protocol Balancer. Over $125 million in Ether and other tokens were stolen.
Regulatory uncertainty
Many global regulators and governments have yet to solidify their policies around cryptocurrency and the staking industry.
While the U.S. has recently taken a pro-crypto stance, other governments have yet to show the same support.
The crypto industry has operated in a regulatory gray area for years, and it’s unclear how regulatory bodies handle certain matters.
Staking versus Other Investment Strategies in the Crypto Market
While staking remains the most popular method to earn passive income, other crypto innovations offer similar opportunities. The rewards, risks, and effort differ among the options.
Liquidity Pools
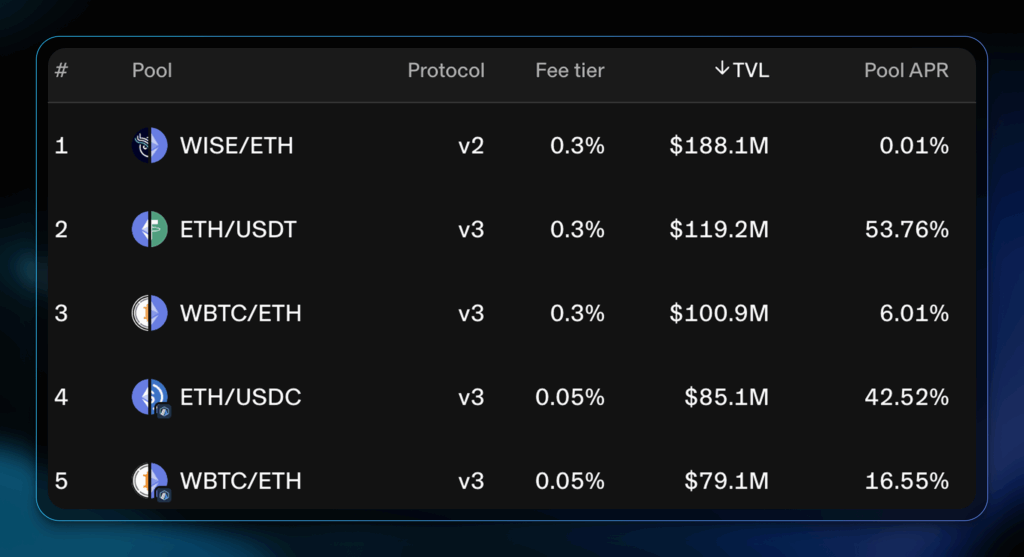
Decentralized exchanges (DEX), such as Uniswap, rely on liquidity pools.
Liquidity pools operate via smart contracts and consist of a basket of tokens (usually a pair of cryptocurrencies). Whenever a user wants to make a trade, smart contracts execute it against the pool.
To encourage investors to deposit cryptocurrency into the pool, DEXs offer rewards. Uniswap offers investors various rates on its pools.
While the effort and returns appear similar to those of ETH staking, users may experience significant losses due to impermanent loss.
Impermanent loss happens when token prices rapidly change, affecting the value of a user’s share in a liquidity pool. Given crypto’s volatile nature, less risk-averse investors may want to tread carefully.
Lending Platforms
Lending platforms operate as decentralized banks. These platforms utilize smart contracts to operate in an automated manner.
Users may earn passive income by depositing their cryptocurrency. The platform then manages the funds and lends them out to borrowers.
Different crypto asset offerings on Kamino
Kamino, a popular Solana lending platform, supports a wide range of stablecoins, including USDC and USDT. Lenders earn over 4% APY by depositing tokens.
In terms of returns, lending platforms rank similarly to staking but offer a wider range of supported tokens.
Whereas staking platforms primarily reward users in the protocol’s native token, lending allows investors to earn rewards even on lower-risk crypto such as stablecoins.
Final Thoughts on the Staking Market
Crypto staking has evolved from a niche alternative to mining into a foundational part of the digital asset economy. Today, it offers investors multiple ways to earn yield while contributing to the security and growth of blockchain networks.
As you get deeper into the space, you’ll encounter networks and protocols fighting to attract your capital. Some of these enticing returns may only last temporarily to acquire more users. You’ll have to act quickly to take advantage of these returns.
That said, staking also carries risks. Make sure to do your research before investing any capital.
To keep up to date with the staking market, check out our staking guides!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Staking Crypto a Good Idea?
Staking allows you to earn passive income on your crypto while helping secure and operate networks. Staking turns your idle assets into yield-generating investments.
Why do People Stake Crypto?
People stake crypto to earn rewards, help secure the network, and potentially increase long-term returns.
Is Crypto Staking Legit?
Yes, crypto staking is a legitimate mechanism used by major blockchains like Ethereum, Solana, and Cosmos. However, staking carries risks, including smart contract exploits and regulatory uncertainty.
Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in February 2024 but has been updated with new information
The content of solostakers.com is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. It represents the personal views and opinions of the author(s) and is not endorsed by any financial institution or regulatory body. Cryptocurrency and staking investments carry inherent risks and readers should conduct their own research and consult with a financial professional before making any investment decisions. The owner and author(s) of solostakers.com will not be liable for any losses, damages, or consequences arising from the use of the information on this site. By accessing solostakers.com, you agree to bear full responsibility for your investment decisions.
January 15, 2026
January 26, 2026