How Staking Safeguards Blockchain Networks

Blockchain technology has revolutionized how we think about digital transactions and data security. Blockchain’s ability to provide a secure and decentralized platform for various applications lies at the heart of its success and eventual mass adoption.
But, how does a blockchain network operate without central authorities and keep the system running?
Staking acts as a key mechanism that contributes to network security.
This article will explore the following:
- What is blockchain staking?
- How does staking secure a blockchain?
- What security challenges do blockchain projects face?
Keep on reading to learn all about staking and blockchain security.
What is Blockchain Staking?
Blockchain relies on multiple entities called validators. These entities replace single authorities and process and validate transactions on the network.
Here’s how staking works:
- Participants, called “stakers,” lock up their cryptocurrency holdings (called the “stake”) to support the operations of a blockchain network.
- Stakers must agree on which transactions go into the network and validate these transactions.
- In return for their contribution, stakers earn staking rewards through newly minted native tokens or transaction fees.
Staking emerged as an alternative to the energy and capital-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
Proof-of-stake (PoS) and Decentralized Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) blockchain networks like Ethereum and Solana utilize the staking consensus mechanism.
Staking’s Role in Blockchain Security
Staking fulfills a vital role in blockchain security by creating a system of checks and balances that helps to ensure network integrity.
Stakers must act honestly and in the best interests of the blockchain because if they act maliciously, they risk losing a part of their stake.
Here’s how staking contributes to blockchain security:
Decentralization
Staking helps increase the decentralization of blockchain networks by allowing a broader range of participants to participate in network validation. This increased decentralization makes it harder for a single figure to control a majority network share and manipulate transactions.
Staking also increases network resiliency. By having validators scattered across the globe, the blockchain continues functioning even if some validators go offline due to unforeseen events.
An investor may look at the network staking participation through the following metrics:
- Validator Count – the number of validators on a blockchain.
- Network Power – the percentage of staked assets held by a validator.
- Staking Ratio – the percentage of available tokens participating in staking.
The higher the validator count and staking ratio, the more involvement from network holders.
Cosmos, one of the largest PoS blockchains, has a Staking Ratio of 50.2%, with $1.25 billion worth of tokens staked. Meanwhile, Coinbase is the top validator on Cosmos with 12.79% of all staked Cosmos.
Penalization
Staking deters malicious behavior because participants must invest capital in the network. If a participant attempts to attack the network, they risk losing a portion of their stake in “slashing.”
Depending on the blockchain network, slashing can result in significant financial loss.
An Ethereum solo staker must stake 32 ETH ($64,000 as of writing) to qualify as a validator. Slashing reduces the staked assets by 1/32 or 1 ETH ($2,000 worth), quite a significant amount. In extreme cases, a staker may even lose the entire stake.
By requiring participants to have skin in the game, staking helps ensure that network participants act in the network’s best interests.
Benefits of Participating in Blockchain Staking
Staking keeps the blockchain secure and operational.
As an industry participant, you should be encouraged to stake as it supports the blockchain space. Without staking, we would not be able to experience the incredible benefits of blockchain networks.
However, staking does incur financial costs. Whether it is the required staking capital or the capital expenditure of setting up your own validator, you do have to spend some money. To compensate for this, staking provides other appealing benefits:
Diversify Digital Assets
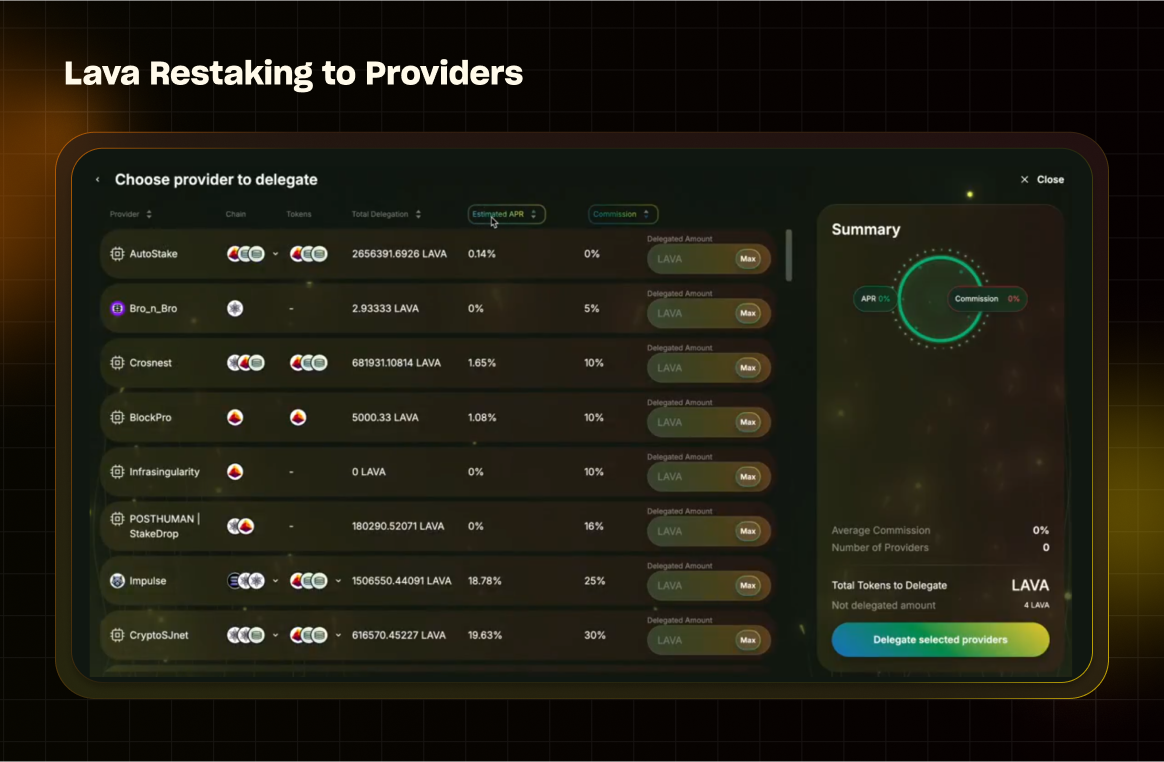
New crypto projects, like Lava Network, offer the opportunity to earn staking rewards in multiple crypto assets. Unlike other projects focusing on creating a new blockchain, Lava manages the data traffic for various blockchains. It provides data optimization rather than building another network.
As shown through Polli.co, a staking optimization platform, you can stake your Lava tokens to Data Providers and earn from a basket of tokens such as Cosmos, Axelar, and Lava.
Earn Passive Income by Staking Crypto
A staker earns staking rewards for keeping the network secure and performing transaction validation. This passive income method is a good way to generate consistent returns on your digital assets, especially if you are not into trading.
You could earn staking rewards of 3% to 20% per annum, depending on which blockchain you choose.
Receive Early-Access Tokens as Staking Rewards
Crypto participants can get new protocol tokens by staking during incentive campaigns. Claiming these airdrop tokens could then lead to enticing financial rewards.
For example, Jito Network, a popular liquid staking platform for Solana (SOL), offered its native token, JTO, to those who staked SOL on its platform. Early backers received over $165 million in Jito tokens, with some users reporting tens of thousands of dollars worth, as the token subsequently listed on popular centralized cryptocurrency exchanges such as Coinbase.
Risks Associated With Staking for Network Security
While staking can provide benefits such as increased security and passive income, it has several risks.
Here are some of the main risks that stakers face:
Illiquidity of Staked Tokens
Staked cryptocurrency is typically locked up for some time.
The stake undergoes an unbonding period to withdraw the funds, which may take up to 30 days, depending on the network. This can be a problem if there is a sudden market downturn or the cryptocurrency is needed for other purposes.
Popular DPOS blockchain Cosmos has an unbonding period of 21 days, making it difficult to access the funds if you are in a hurry.
Some developers have tackled this illiquidity challenge through Liquid Staking. Read our guide to learn more about it.
Regulatory Uncertainty for Staking Crypto
Staking is relatively new, and regulations are continuously evolving. There is a risk that regulators may crack down on staking or impose restrictions that could impact profitability or accessibility.
In June 2023, centralized exchange Coinbase withdrew its staking services in several U.S. states after a regulatory crackdown.
Security Challenges Faced by Blockchain Networks
Despite the security benefits offered by blockchain technology, blockchains are not immune to security challenges. Such is the difficulty faced in operating in the technological sector.
Here are some security challenges in the blockchain space:
DDoS Attack
When trying to access a popular website during high-traffic times, you may have experienced slowdowns and network unavailability issues.
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack floods a network or server with traffic, making it unavailable to its intended users. It mimics the same high-volume activity experienced by sites during high traffic.
DDoS attacks can damage blockchain networks by preventing validators from accessing and overloading the network, causing it to become unstable or fail.
Manta Network, a new modular blockchain, witnessed a DDoS attack during its maiden exchange token listing. The attack severely impacted token withdrawal times and network speed.
51% Attack
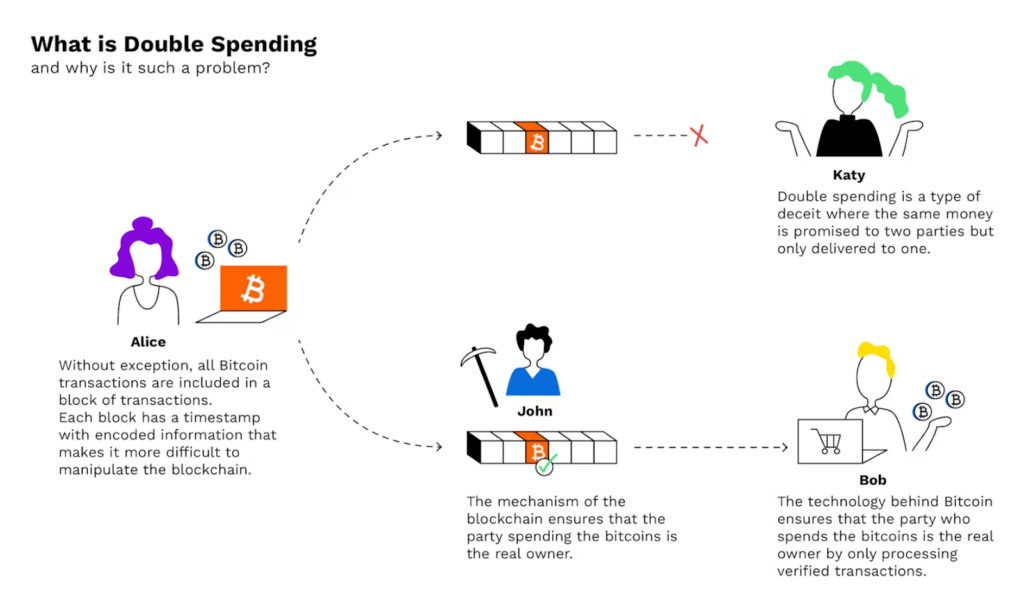
In a Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain, a 51% attack refers to a scenario where a single entity or group of entities controls more than 50% of the total stake in the network. This control allows them to manipulate the transaction history and double-spend coins.
Double-spending means the same cryptocurrency units could be spent twice, which is an issue facing digital transactions.
To double-spend coins, the attacker would first send coins to a party. Once the transaction is confirmed, the attacker would manipulate the transaction history by creating a new block that excludes the original transaction. This would reverse the transaction and allow the attacker to spend the coins again.
Conclusion: Staking is the Key to Blockchain Security
While staking has become synonymous with passive income, it is, first and foremost, a consensus mechanism that contributes to network security. It incentivizes network participants through staking rewards and penalizes malicious behavior through slashing.
Furthermore, staking keeps the network resilient by decentralizing its validator network.
If staking and its ability to earn passive income have caught your attention, read more of our staking guides at Solo Stakers.
Happy Staking!
The content of solostakers.com is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. It represents the personal views and opinions of the author(s) and is not endorsed by any financial institution or regulatory body. Cryptocurrency and staking investments carry inherent risks and readers should conduct their own research and consult with a financial professional before making any investment decisions. The owner and author(s) of solostakers.com will not be liable for any losses, damages, or consequences arising from the use of the information on this site. By accessing solostakers.com, you agree to bear full responsibility for your investment decisions.
March 22, 2024
July 3, 2025