Exploring Cross-Chain Staking
Imagine you have credit cards from two different banks, Bank A and Bank B, each with its loyalty program offering exclusive benefits.
Bank A offers cashback rewards for using its card for specific purchases. Bank B provides travel rewards points for transactions made with its card.
Picture a third-party platform that lets you exchange Bank A’s rewards with Bank B’s and vice versa. This way, you can benefit from the combined rewards of both banks.
Through cross-chain staking, users can deposit their staking assets on one blockchain, receive rewards, and participate in activities on multiple chains. While it’s a new concept, developers have begun looking into it as more networks continue to rise.
Learn what cross-chain staking is, how it works, and the benefits and risks from this guide.
What is Cross-Chain Staking?
Before discussing cross-chain staking, it is essential to tackle interoperability.
Most blockchains work in isolation and are written in different languages and frameworks. Ethereum uses an ERC-20 token standard, while Bitcoin operates on BEP-20. Owning cryptocurrency on Ethereum does not enable direct transfer to networks like Bitcoin.
Whatever develops for one network cannot be used for another. Similarly, users must choose which blockchain to leverage their digital assets. This lack of interoperability hampers innovation and fragments liquidity within the blockchain space.
What is Cross-Chain Interoperability?
Cross-chain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate, share data, and operate in a coordinated manner. Interoperability enables seamless interaction between various blockchain platforms.
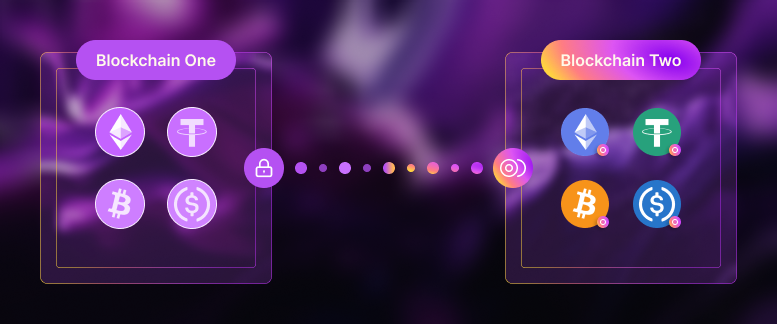
Cross-chain technology facilitates interoperability by acting as a bridge between two distinct blockchains. Cross-chain links allow users to move assets between different chains.
Transactions are executed through smart contracts (self-executing code). These protocols secure your crypto assets in a pool and return an equivalent cryptocurrency compatible with the other network. This process is known as “wrapping.”
As a sample, the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) industry is predominantly based on Ethereum. Users from other networks become locked out of the full benefits of the DeFi space.
With a cross-chain bridge, A BEP-20 Bitcoin can be wrapped and transferred to Ethereum to become an ERC-20 Bitcoin. Then, Bitcoin can be used throughout the Ethereum DeFi ecosystem.
How Does Cross-Chain Staking Work?
Cross-chain staking would involve staking in one network (such as Ethereum) and receiving rewards in another (Solana). However, current blockchain technology has yet to solve this.
In its current form, cross-chain interactions are executed via DeFi protocols, specifically through liquid staking solutions.
Liquid staking is a process defined as follows:
- Stakers deposit their cryptocurrency on a third-party liquid staking platform.
- The deposited token is pooled and goes on to perform network validation.
- Stakers receive liquid staking tokens (LST), equivalent to their staking capital. These LSTs represent the staked assets in a blockchain network that provide liquidity.
- Users can then transfer the liquid staking tokens to another blockchain, where they can be used for other staking activities.
Through cross-chain liquid staking solutions, users fully participate in staking activities across two or more blockchains.
How Does Cross-Chain Staking Differ From Traditional Staking?
Cross-chain and traditional staking allow users to participate in the network’s operations and earn rewards by locking up their crypto assets. However, they differ in their mechanism and the networks involved.
Traditional staking, especially solo staking, entails a user staking and participating on a single network without relying on third parties. Cross-chain staking uses pooled staking and relies on smart contracts and DeFi applications.
What is an Example of Cross-Chain DeFi?
Lido Finance is the largest liquid staking platform with over $22.5 Billion in total value locked (TVL). Stakers deposit Ethereum and receive liquid staking tokens called stETH in return. Since Lido operates on Ethereum, users cannot use stETH across the greater DeFi landscape.
In September 2023, Lido announced it would bridge stETH to the Cosmos ecosystem, enabling interoperability. Through a collaboration with Neutron and Axelar, stakers could operate on multiple chains.
Here’s a breakdown of the cross-chain DeFi process:
- Stakers participate in liquid staking by depositing ETH onto Lido and receiving stETH.
- Users wrap stETH into wstETH through Lido’s wrapping widget
- Using Neutron Bridge, a user bridges wsETH on Ethereum to wstETH on Cosmos (note that a user must connect an Ethereum and Cosmos wallet).
- A user can now engage in passive income strategies across Cosmos.
Without cross-chain DeFi, a staker can only use their stETH in the Ethereum ecosystem. This removes them of opportunities such as yield farming Neutron and wstETH on Astroport (a Cosmos DeFi hub).
Emerging Platforms for Cross-Chain Staking
Some platforms have attempted to innovate the space by offering cross-chain staking rewards. While not cross-chain staking perse, a staker can deposit tokens from a single network and get rewards across multiple chains.
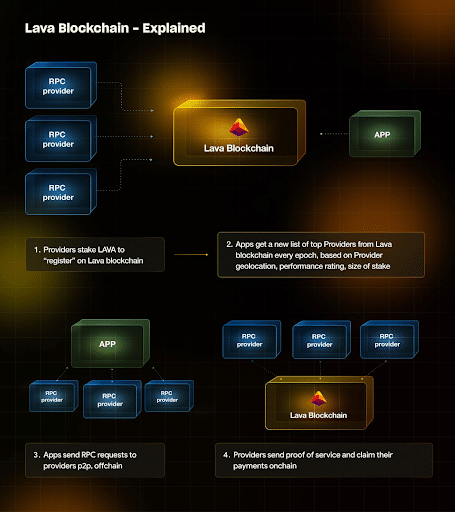
Lava Network is pioneering cross-chain staking by incentivizing users to stake their LAVA tokens to power the network and restake their LAVA to power RPC Node providers. When a Lava Network staker restakes their LAVA tokens to a Provider, the former can get cross-chain staking rewards in other networks such as Cosmos and Axelar.
Note that RPC providers power the data, which flows through blockchains. Meanwhile, restaking is a popular concept in Ethereum that allows users to utilize already staked assets to secure other blockchain projects.
What Benefits Does Cross-Chain Staking Offer to Crypto Investors?
Cross-chain technology offers several benefits that contribute to decentralized ecosystems’ overall efficiency and functionality.
Here are a few benefits of cross-chain staking:
Optimized Returns
Users can maximize their digital assets by choosing the most rewarding staking opportunities across blockchains. Stakers can adapt to changing market conditions and seek higher yields.
Returning to the example of bridging wstETH from Ethereum to Neutron, a staker can earn 20.80% APR on Neutron and wstETH liquidity pools. Such opportunities are absent outside the Cosmos ecosystem.
Enhanced User Control
Users have greater freedom and control over their crypto assets.
They can choose the blockchain that aligns with their preferences, risk tolerance, or investment strategy. Users can actively manage their assets and stake on multiple blockchain networks.
Risks Associated With Cross-Chain Staking
While cross-chain interoperability presents various benefits but comes with risks and challenges.
Make sure to perform due diligence before engaging in cross-chain staking.
Security Risks
Interacting with multiple blockchains introduces various attack vectors. Security vulnerabilities in one blockchain or within the cross-chain infrastructure could expose users’ assets to risks.
Furthermore, users must click through various sites to fulfill staking across blockchains. This raises the potential for clicking dubious sites and malicious links.
Smart Contract Risks
Cross-chain staking involves using smart contracts to facilitate asset transfers and activities between blockchains. Smart contracts possess vulnerabilities, coding errors, and exploits that could lead to financial losses.
In February 2022, Wormhole Bridge (one of the more popular cross-chain bridges between Solana and Ethereum) experienced a security exploit that resulted in $321 Million in losses. A hacker minted millions worth of wETH on Solana and then redeemed wETH for ETH on Ethereum alongside other tokens. The hack was the then-second-largest DeFi attack in history.
Which Blockchains Currently Support Cross-Chain Staking?
Multiple blockchains support cross-chain activities, providing for seamless interoperability.
Hop Protocol is a cross-chain bridge application that allows users to send popular cryptocurrencies such as USDT, USDC, and Ethereum across various networks. Here are a few examples of networks it services:
- Arbitrum
- Base
- Ethereum
- Linea
- Polygon
Aside from bridging digital assets, Hop Protocol provides yield farming with various token pools.
As long as infrastructure and DeFi applications support the blockchain, users can navigate the DeFi landscape.
Market Size of the Cross-chain DeFi Ecosystem
Cross-chain DeFi has mostly recovered since the market lows in May 2022.
For example, popular bridges such as Wormhole have attracted over $1.0 Billion in TVL. Ethereum, Sonic (formerly Fantom), and Solana remain the most used cryptocurrencies on the bridge. Since its inception, the cross-chain protocol has processed over $38.0 Billion in cross-chain transfers.
As more and more networks are developed, users can expect the cross-chain landscape to get bigger.
Conclusion
Cross-chain staking has the potential to reshape the landscape of decentralized finance. Imagine an interconnected blockchain industry where users can freely diversify digital assets and capitalize on opportunities across multiple blockchains.
As with any innovation, there will be risks. More recent security incidents have revealed that users must approach with cautious optimism and exercise operational security at all times.
While hurdles may mark the road ahead, the transformative promise of a cross-chain blockchain world keeps the industry wide-eyed with big expectations!
Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in March 2024 but has been updated with new information
The content of solostakers.com is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. It represents the personal views and opinions of the author(s) and is not endorsed by any financial institution or regulatory body. Cryptocurrency and staking investments carry inherent risks and readers should conduct their own research and consult with a financial professional before making any investment decisions. The owner and author(s) of solostakers.com will not be liable for any losses, damages, or consequences arising from the use of the information on this site. By accessing solostakers.com, you agree to bear full responsibility for your investment decisions.
March 4, 2025
August 4, 2025