The Truth About Ethereum Staking

With the cryptocurrency market finally rebounding off its late-2022 lows, investors have been looking for ways to maximize their crypto assets further.
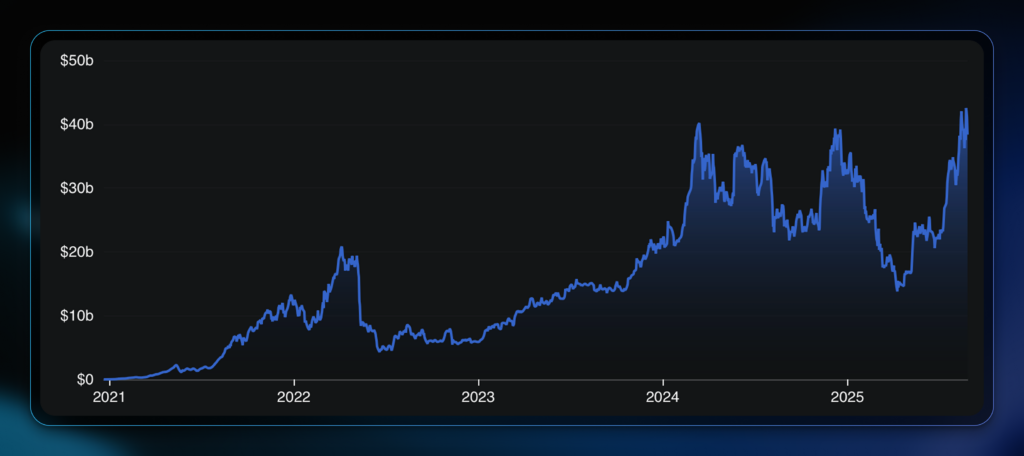
Crypto staking has re-emerged as a popular way to make passive income and earn airdrops to new networks and protocols. Staked ETH has a market capitalization of $100 Billion, an outstanding 200% growth over the past year. The Ethereum network is by far the most popular network to stake on.
However, beneath this positive exterior, lies a complex governance system.
Recent proposals to adjust the issuance curve of Ethereum staking rewards have left the community debating on the decentralized nature of the Ethereum network. The Ethereum Foundation, the main governance body behind Ethereum, appears to act like the same central bankers blockchain sought to eliminate.
Ethereum staking participants can find these arguments confusing, preventing them from further investing or leaving the Ethereum staking market entirely.
So it’s time for another guide.
In this article, we will tackle all about staking ETH:
- What is ETH staking
- How much you can earn with Ethereum staking
- The different ways to stake ETH
- Ethereum governance
…and much more
It’s time for a deep dive on staking Ethereum!
What is ETH Staking?
Staking involves engaging in the staking consensus mechanism utilized by blockchain networks. Blockchain relies on a decentralized network of computers to validate transactions. This network must agree on what transactions get recorded into the blockchain; thus, the term consensus mechanism.
In traditional Ethereum solo staking, the staking process occurs via the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus.
You set up computer hardware (called a validator node) that operates the necessary blockchain software. You then connect to the Ethereum network, stake ETH, and validate transactions.
You receive staking rewards in the form of fresh ETH tokens.
Staking Ethereum vs Mining
Staking and Mining (known as Proof-of-Work) are different methods for validating transactions and securing blockchain networks. Earlier cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin rely on mining. Before transitioning to staking in 2022, Ethereum also utilized a mining consensus.
Newer networks, such as Solana, Cardano, and Polkadot, use staking.
Mining
Miners race against each other to solve complex mathematical problems in order to validate transactions (stored in a block) and receive new coins as a reward.
As Bitcoin has a finite supply of 21 million tokens, Satoshi Nakamoto (the anonymous creator) programmed for the rewards to diminish over time, approximately every 4 years. During this time mining rewards are halved in the highly anticipated event called the halving.
The latest halving occurred on April 19, 2024.
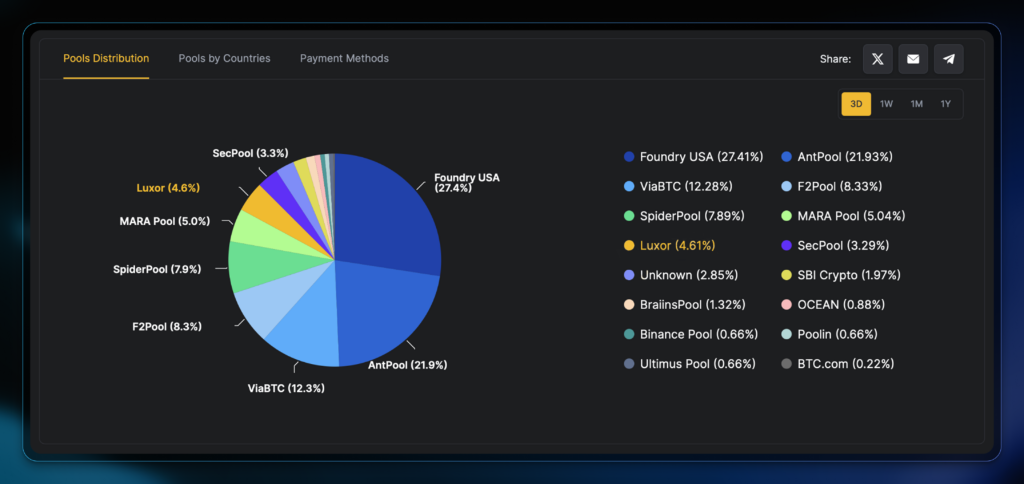
Because of the halving process, miners become even more competitive and upgrade their computer equipment or pool together. This arms race for the most computing power requires large energy consumption and centralization.
Close to 50% of the Bitcoin mining power is now controlled by just 2 entities – AntPool and Foundry USA Pool.
Staking ETH
To combat the issues faced by mining, blockchain developers created staking.
While staking is considered to be more accessible than mining, it still requires hardware and technical expertise. And remember how the minimum stake is 32 ETH? That’s approximately $100K as of writing, not exactly affordable.
Enter the beauty of blockchain innovation.
Developers have created innovations to enable stakers of all sizes to combine crypto assets and participate in staking.
Note: Other networks, such as Polkdaot have embraced Delegated-Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) to make the staking process more affordable to participants. As this exists outside of Ethereum, we won’t be discussing it here. Instead read our guide on how to become a staker without having a staking operation.
The Different Ways to Stake ETH
Technical stakers can pursue a solo staking route. On the other hand, non-technical participants can also maximize their crypto assets without having the technical know-how to set up a staking operation.
Numerous platforms cater to the non-technical crowd by providing a seamless experience that can be accessed with just a wallet or exchange account.
Solo Staking ETH
Solo staking is the purest form of Ethereum Staking. You stake Ethereum blockchain without relying on a third party or a staking pool to do so.
To simplify the steps of staking ETH:
- You setup your own node, which operates and stores a copy of the Ethereum blockchain. Nodes contribute to the overall decentralization of the Ethereum network by having various machines worldwide store a copy of the network’s data.
- To start earning ETH staking rewards, you transform this node into a validator node, by depositing 32 ETH. By having a deposit, you now have skin in the game. Beware that malicious validators can lose a portion of their stake through slashing.
- In return for validating transactions, you receive staking rewards.
As solo staking requires you to operate your own validator 24/7, you incur recurring operating expenses such as electricity, data plans, and for some cloud hosting costs. It’s like running your own business.
To keep tracking of your revenues (staking rewards) and expenses, it’s suggested to use a staking dashboard.
A staking dashboard connects to your own validator node and allows you to keep track of earnings as well as the technical performance of your machine. Many dashboards also possess the ability to alert you on Telegram and Slack.
Staking-as-a-Service Platforms (SaaS)
SaaS is a form of staking wherein an intermediary handles the hardware and software requirements of staking. Third parties handle the node and validator operations on behalf of stakers for a fee.
You choose a staking provider, lock up 32 ETH, and receive staking rewards. In this process, you maintain control of staked crypto by possessing the withdrawal keys. However, the validator credentials are handed over to the third party for validation.
With the professional customer service and security provided by large SaaS providers such as Stake.fish, more affluent stakers may prefer to go down this route.
With the help of a staking calculator, you can estimate your staking rewards. According to Stake.fish’s calculator, your 32 ETH would grow by 3.45% or 1.104 ETH over the course of one year.
Staking Pools
A staking pool makes staking accessible to virtually anyone, as they require very minimal staked ETH. An operator or administrator manages the pool and maintains the validator node. Meanwhile, rewards are handed out based on the amount and duration staked within the pool.
Smart contracts run the pool in a trustless and automated environment and anyone can stake using a non-custodial wallet such as Metamask.
Lido Finance operates one of the largest Ethereum staking pools with its liquid staking platform.
With liquid staking, a holder deposits their ETH and receives a liquid staking token (LST) of equivalent value in return. In the case of Lido, you deposit ETH and receive the liquid token stETH, which can be used in trading and decentralized finance applications. Lido takes a 10% fee for managing the platform.
Lido has become extremely popular, coming a long way since it first emerged in 2021. As of writing, approximately 20% of all staked ETH resides with Lido.
Restaking Protocols
Restaking allows you to reuse staked ETH to contribute to the security of other decentralized applications and projects. Restaking allows you to optimize a single group of staked assets and earn high returns.
EigenLayer is one of the most Ethereum restaking protocols with $20 billion in total value locked.
Issues with Ethereum Governance
With all the different ETH staking modes and the general increase in staking participants, you would think that all is well with Ethereum. After all, the more stakers involved, the better, right? The network would be more secure. But it’s not that straightforward.
Ethereum researchers argue that at the current state, eventually, stakers will deposit all ETH via liquid staking due to their attractiveness to everyday stakers. This outcome poses a couple of problems:
- Winner-take-all: Like many financial industries and applications, liquid staking will drift towards a singular platform. Thus, staked ETH would be centralized, posing the same problems as mining.
- Too big to fail: The biggest liquid staking platform would grow into a system of apps and protocols and may become too big to fail, mimicking large financial players in the fiat world. Ethereum governance proposals would then have to consider these platforms..
- Sound money-ness: Liquid staking places LSTs into the hands of stakers. As liquid staking adoption grows, the centralized LST replaces the decentralized Ethereum, placing undue risk on stakers.
To address these problems, the Ethereum Foundation has proposed a change to the way stakers earn ETH rewards. But a central body dictating Ethereum monetary policy feels all too familiar.
Suddenly, what ought to be a decentralized industry looks just like traditional money.
Frequently Asked Questions
Interested in Ethereum staking? Here are some other FAQs that you may need the answer to.
How Much Will You Earn by Staking Ethereum?
Ethereum staking has an annual yield of 2.9%. The return may slightly differ based on which platform you’re using and whether or not they charge commission or provide additional rewards.
Assuming you stake 10 ETH, you would get 0.29 ETH after a year, translating to $1,300 in staking rewards.
Can I Lose My ETH if I Stake it?
You cannot lose your entire staked ETH through the regular staking process. You can lose a portion of it however through slashing, a process that punishes malicious validators. Slashing typically takes 1/32 ETH of a validator.
However, should you be staking with a third-party application and protocol, you could lose your entire stake through malicious actors. You could lose your entire crypto by connecting to a malicious link or if the protocol gets drained by a bad actor.
Should I Stake Ethereum on Coinbase?
Coinbase ETH staking returns 1.86% per year, much lower than the network’s rewards due to the exchange’s commission rates. Some participants may choose to stake with centralized exchanges (CEX) due to familiarity or the exchange’s security.
For those unwilling to take self-custody of their assets or pursue solo staking, using a CEX is a good option.
Is Staking Ethereum Still Worth It?
Ethereum staking provides staking returns of 2.9% per annum. While that may not sound so great, it is great to earn yield on your staked assets.
Instead of holding your ETH idly in your crypto wallet, you can engage in staking, participate in network security, and earn staking rewards.
Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in May 2024 but has been updated with new information.
The content of solostakers.com is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. It represents the personal views and opinions of the author(s) and is not endorsed by any financial institution or regulatory body. Cryptocurrency and staking investments carry inherent risks and readers should conduct their own research and consult with a financial professional before making any investment decisions. The owner and author(s) of solostakers.com will not be liable for any losses, damages, or consequences arising from the use of the information on this site. By accessing solostakers.com, you agree to bear full responsibility for your investment decisions.
August 28, 2025
September 1, 2025